In the world of packaging and manufacturing, the need for efficient and reliable sealing methods
has led to the development of varioustechnologies. Among the most commonly used methods are
ultrasonic sealing and heat sealing. Both of these processes are pivotal inensuring product integrity,
especially in industries that require airtight or tamper-proof seals. But how do these two sealing
methods compare in terms of efficiency, cost, and practicality?
This article provides an in-depth comparison of ultrasonic sealing and heat sealing, examining their
advantages, challenges, and the
situations in which each method excels.
Understanding the Sealing Processes
Before diving into the differences between ultrasonic and heat sealing, let’s take a moment to understand
how each process works.
What is Ultrasonic Sealing?
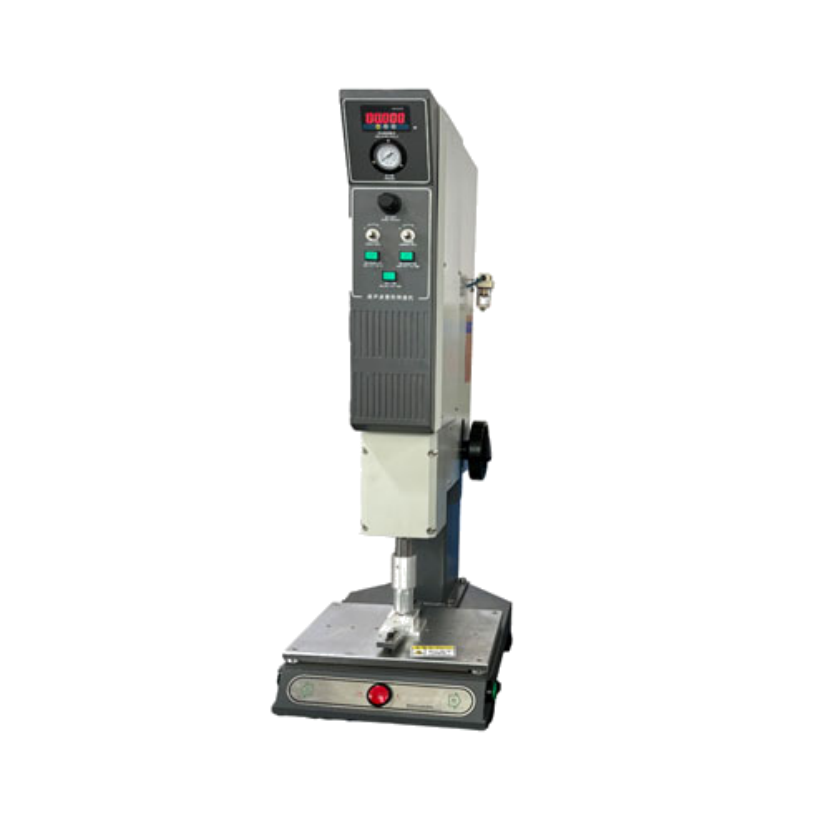

Think of ultrasonic sealing as using sound waves to bond materials together. Sounds pretty cool, right?
Here’s how it works:
an ultrasonic machine sends out high-frequency vibrations — kind of like a super-fast buzzing sound that’s
too high-pitched for us to hear.These vibrations cause the molecules in the thermoplastic (or whatever
material you're using) to start moving really fast. When the thermoplastic molecules vibrate, they get
warmer and soften.Once they’re soft enough, the material is pressed together by a tool called
an “anvil,” and voilà — the materials bond at a molecular level, creating a solid, durable seal.
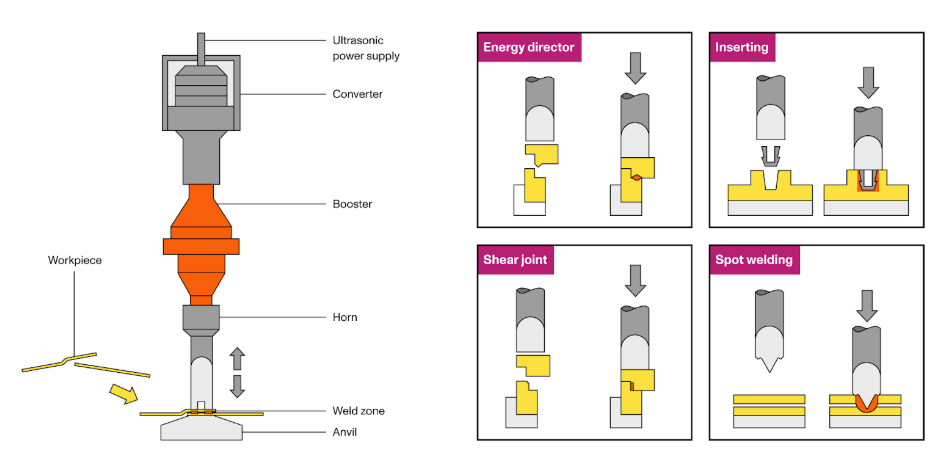
This process happens super quickly, usually in a fraction of a second, and it doesn’t need any external
heat to get the job done.That’s one of the reasons why it's such a great choice for packaging sensitive products.
What is Heat Sealing?

Heat sealing is a bit more familiar and relies on good old-fashioned heat. In this method, press head
(usually called welding head and heating by heading tubes) is heated up to a high temperature.
When the thermoplastic (or other materials) is placed at bottom workpiece under certain pressure,
the heat softens the thermoplasticOnce the thermoplastic is soft enough,
the heated head press the materials together. As they cool, the material hardens, forming a seal.
It’s a tried-and-true method that works well for many products, but the catch is that the heat can sometimes
be too much for delicate items or materials that aren’t heat-resistant. Plus, the machine needs to stay hot,
which can be inefficient and add extra time to the process.
Challenges Associated with Heat Sealing
While heat sealing has been a standard in many industries, it does come with its own set of challenges.
Some of the common issues with heat sealing include:
1. Heat-Up Time
Heat sealing machines need to be preheated to reach the necessary temperature before they can begin sealing.
This process can take time, especially at the beginning of shifts or after extended periods of inactivity.
This delay can reduce overall production efficiency and may require additional waiting time at the start of
a production run.
2. Excess Heat During Operation
The metal sealing jaws used in heat sealing remain hot even after the sealing process is completed.
This introduces a safety risk, as workers may accidentally come into contact with these heated surfaces.
Moreover, the residual heat can prolong post-production cooling periods,
adding time to the overall manufacturing cycle.
3. Leakage and Contamination
Heat sealing can lead to higher leakage rates, particularly in products containing liquids or semi-solids.
Items like salads, sauces, juices, and soups are prone to leaking during the sealing process because
the heat applied can interfere with the sealing area, causing inconsistent results.Additionally,
contaminants such as oil or product residue on the sealing surface can compromise the seal quality.
Advantages of Ultrasonic Sealing
Given the challenges associated with heat sealing, ultrasonic sealing offers several compelling benefits.
The following advantages make ultrasonic sealing an attractive option for many manufacturers:
1. Less Packaging Waste
One of the standout benefits of ultrasonic sealing is its ability to create a narrow, precise seal with
minimal material use. This results in less waste during production, which is particularly advantageous
for companies that require large quantities of packaging material. By reducing raw material usage,
ultrasonic sealing can generate significant cost savings over time. Additionally, the smaller seal area is
ideal for reducing material costs while maintaining package integrity.
2. Lower Energy Consumption
Unlike heat sealing, ultrasonic sealing doesn’t require continuous heat to operate. The energy is used
only when the ultrasonic vibrationsare activated, which means energy consumption is significantly lower.
In contrast, heat sealing systems often consume energy even when idle, as the heated jaws remain warm
between sealing cycles. This makes ultrasonic sealing a more energy-efficient solution for many facilities.
3. Preservation of Heat-Sensitive Products
Ultrasonic sealing is particularly beneficial for heat-sensitive products, including chocolates, cheeses,
and certain pharmaceutical items. Because no heat is applied directly to the product,
it prevents damage from excessive temperatures. This helps preserve the integrity of the
product and reduces waste due to spoilage or heat degradation.
4. Reduced Maintenance Requirements
Ultrasonic sealing systems typically require less maintenance compared to heat sealing machines.
Since ultrasonic systems are less exposed to the repetitive heating and cooling cycles that wear
down traditional sealing equipment,they have a longer operational life and experience
fewer mechanical issues. Additionally, fewer consumable parts need to be replaced, which reduces
downtime and maintenance costs.
5. Superior Sealing Quality
Ultrasonic sealing creates a bond at the molecular level, which leads to more precise and stronger seals.
This process ensures the elimination of leakage and enhances the overall performance of the seal.
Moreover, ultrasonic sealing is effective in sealing through product residuesuch as oils, liquids,
or powders, making it ideal for a wide range of applications. This can be especially beneficial
in preventing product contamination and extending the shelf life of products.
6. Greater Versatility
Ultrasonic sealing offers the flexibility to bond various types of materials, such as thermoplastics, films,
and even multilayer structures. Because the process doesn’t rely on heat, it can be used for
a wider range of materials, including heat-sensitive films that would be compromised under
conventional heat sealing. This versatility is particularly useful in packaging operations that deal
with diverse product types.
Costs & Return on Investment (ROI)
The initial investment in ultrasonic sealing equipment is typically higher than that of heat sealing systems.
However, over time, ultrasonic sealing provides significant cost savings in several key areas:
1. Raw Material Reduction
Ultrasonic sealing’s ability to create smaller, more precise seals means less material is required,
both in terms of sealing area and overall packaging. For manufacturers, this translates to
reduced material costs and less waste, which is a major advantage in high-volume production
environments.
2. Energy Efficiency
Since ultrasonic sealing does not rely on constant heat, it significantly reduces energy costs.
Unlike heat sealing, where machines continue to consume power even when idle, ultrasonic systems
only draw power during the actual sealing process. This makes ultrasonic sealing a
more cost-effective option in the long run.
3. Reduced Maintenance Costs
Due to the lower mechanical wear and tear on ultrasonic sealing systems, maintenance costs are reduced.
Heat sealing systems, on the othe hand, face the challenge of frequent replacements and repairs of heated components,
which can add to the overall cost of ownership.Over time, the reduced need for repairs and downtime
with ultrasonic sealing systems results in a higher return on investment (ROI).
4. Increased Speed and Efficiency
Ultrasonic sealing is also faster than heat sealing, as it can seal multiple units per minute, increasing
production throughput. This efficiencyhelps reduce the cost per unit and can be a decisive factor for manufacturers
looking to scale operations quickly.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Sealing Method
When deciding between ultrasonic sealing and heat sealing, manufacturers must consider their specific
product requirements, productionvolume, and material types. Heat sealing may still be the preferred
choice for applications where high temperatures are acceptable and production speed is a priority. However,
for industries dealing with sensitive products,higher energy costs, and the need for precision,
ultrasonic sealing presents a superior alternative.By weighing the pros and cons of each method,
manufacturers can make informed decisions that will optimize their production efficiency,
reduce costs, and enhance product quality in the long term.
Phone: +86-15989541416
E-mail: michael@sztimeast.com
Whatsapp:+86-15989541416
Add: 3/F, Building 5,Huixin Intelligent Industrial Park, Xinhu, Guangming, Shenzhen,China 518107
We chat